Loading Data
Learn how to load DICOM files from local sources and cloud storage into the Avara Viewer.
Introduction
Section titled “Introduction”The Avara Viewer supports loading DICOM data from multiple sources, automatically organizing files into studies and series for easy navigation. You can load data from local files on your computer or from cloud storage using presigned URLs.
Local files can be loaded by dragging and dropping individual files, folders, or zip archives directly into the viewer. The viewer processes only DICOM files, automatically filtering out non-DICOM content.
When configured with cloud data URLs, series data streams in automatically with a progress indicator. Enhanced DICOM series become interactable immediately, while interoperable DICOM series require the entire study to finish loading before becoming interactable. Streaming is fast and highly optimized for efficient data transfer.
Once data loading is initiated, additional data cannot be loaded after the fact unless the user refreshes the tab back to an empty viewer.
For mammography studies, the viewer automatically detects MG modality during parsing and invokes a specialized hanging protocol that intelligently arranges series in optimal layouts based on study content and comparison availability.
Local Files
Section titled “Local Files”You can load DICOM files directly from your local machine by dragging and dropping files, folders, or zip archives into the viewer, or by browsing your device to upload files. The viewer automatically processes only DICOM files, filtering out any non-DICOM content.
Supported input formats include individual DICOM files, folders containing DICOM files, and zip archives containing DICOM files. The viewer will automatically organize series and studies from your selected files.
Cloud Data URLs
Section titled “Cloud Data URLs”When configured with cloud data URLs, series data streams into the viewer automatically with a progress indicator. Once the viewer is opened, no additional user actions are needed – the data loads seamlessly in the background.
Enhanced DICOM series become interactable immediately as they stream in, allowing you to begin viewing and manipulating images without waiting for the entire study to complete. Interoperable DICOM series require the entire study to finish loading before becoming interactable. Streaming is fast and highly optimized for efficient data transfer and minimal latency.
Mammography
Section titled “Mammography”When MG (mammography) modality is detected during DICOM parsing, the viewer automatically invokes a specialized hanging protocol that intelligently arranges series in optimal layouts based on study content and comparison availability.
Hanging Protocol
Section titled “Hanging Protocol”The mammography hanging protocol uses a rules engine to determine the optimal layout and series assignment. A valid study must contain at least one series matching L CC, L MLO, R CC, or R MLO views that are not partial and do not have view modifiers (except ID, NP, or modifiers containing “synth”).
The protocol selects the most recent valid study as the current study and the next most recent valid study as the comparison study. The hanging protocol priority is checked in the following order:
- DBT current + DBT prior → 2x4 Layout: If the current study contains DBT (Digital Breast Tomosynthesis) series and a prior study also contains DBT series, use a 2x4 layout comparing current DBT to prior DBT.
- DBT current + 2D synth current (same study) → 2x4 Layout: If the current study contains both DBT and 2D synthetic series, use a 2x4 layout for internal comparison within the same study.
- DBT current + 2D non-synth current (same study) → 2x4 Layout: If the current study contains both DBT and 2D non-synthetic series, use a 2x4 layout for internal comparison within the same study.
- DBT current alone (ignore 2D priors) → 2x2 Layout: If the current study contains only DBT series with no DBT prior study, use a 2x2 layout. Any 2D prior studies are ignored.
- 2D current + 2D non-synth prior (ignore DBT priors) → 2x4 Layout: If the current study contains 2D series and a prior study contains 2D non-synthetic series, use a 2x4 layout. Any DBT prior studies are ignored.
- 2D current + 2D synth prior (ignore DBT priors) → 2x4 Layout: If the current study contains 2D series and a prior study contains 2D synthetic series, use a 2x4 layout. Any DBT prior studies are ignored.
- 2D current alone (ignore DBT priors) → 2x2 Layout: If the current study contains only 2D series with no 2D prior study, use a 2x2 layout. Any DBT prior studies are ignored.
Key constraints: DBT current studies never compare to 2D prior studies (only DBT prior or 2D within the same study), and 2D current studies never compare to DBT prior studies (only 2D prior). When multiple series match a position, the protocol prefers DBT over 2D, then synthetic vs source based on context, with lower series number as a tie-breaker.
The hanging protocol may yield between 0 and 6 empty viewports depending on the nature of the series available in the study. This is expected behavior – not a bug – as the protocol only assigns series that match the required view positions (L CC, L MLO, R CC, R MLO). If a study doesn’t contain all four standard views, the corresponding viewports will remain empty.
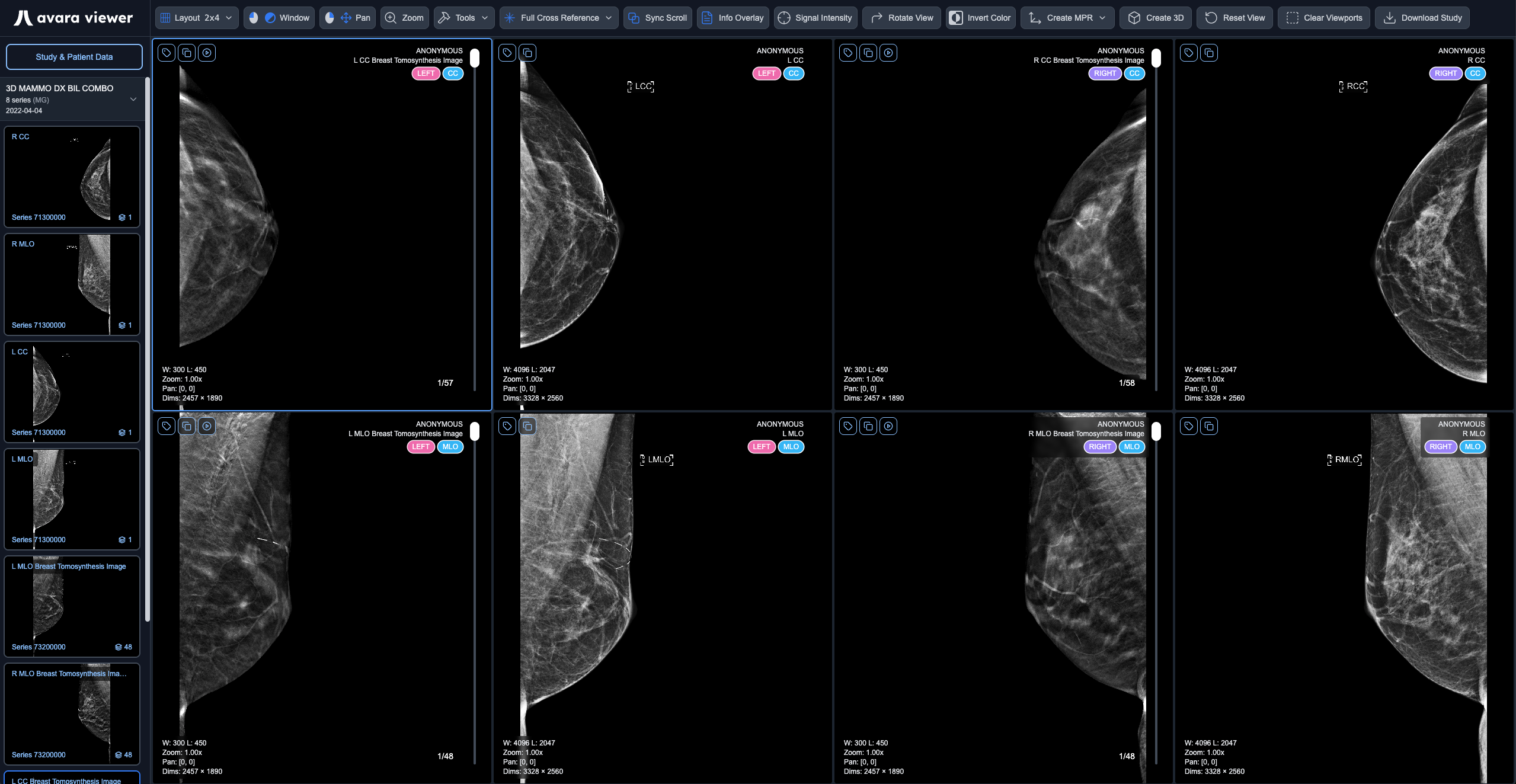
Display Tags
Section titled “Display Tags”Each mammography series displays specialized colored tags in the top right corner of the viewport, providing quick visual identification of key series attributes. The tags render in the following order:
- LATERALITY - Indicates which breast: Left (pink) or Right (purple)
- VIEW - The imaging view type: CC or MLO (blue)
- VIEW-MODIFIER - Additional view information if present (green)
- PARTIAL - Only shown if present: Partial view indicator (yellow)
These color-coded tags enable radiologists to quickly identify and distinguish between different series and views at a glance, improving workflow efficiency during mammography reading sessions.

Ex. This tag display is for a left CC implant displaced partial view
